Phone:
(701)814-6992
Physical address:
6296 Donnelly Plaza
Ratkeville, Bahamas.

A DIY hydroponics tower is a vertical gardening system that grows beautiful plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water to keep roots healthy. Many first-time growers are interested in this method because it saves space, uses less water, and delivers fresh harvests year-round. Still, questions about how to build, set up, and maintain a tower can stop beginners from starting. This guide explains what a hydroponics tower is, the benefits of building one yourself, the components you need, and how to keep it running efficiently.
A DIY hydroponics tower is a self-built vertical growing system where plants are stacked in levels, with their roots exposed to a constant flow of nutrients. Instead of soil, the roots grow in a controlled water-based environment, which helps maximize plant growth in small spaces.
Builders often refine their setups by following Hydroponics360 vertical garden techniques, which outline practical methods for nutrient delivery, plant spacing, and water flow adjustments. These insights help even first-time growers create productive and stable systems that match their space and budget.
For example, a balcony gardener in Seattle built a four-foot PVC tower for basil, lettuce, and mint. The design allowed consistent harvests without taking up more than a few square feet of space, proving how compact these systems can be.
DIY hydroponics towers offer versatility that fits a variety of spaces and purposes. Unlike fixed commercial systems, homemade towers can be tailored to specific crops and available space. They also make it easier for growers to experiment with plant combinations, seasonal adjustments, and custom nutrient schedules.
Urban rooftop farms, school greenhouses, and small restaurant suppliers often use homemade towers to produce herbs and greens. In Chicago, a community project constructed several towers to supply fresh basil and parsley to local chefs, proving the model’s practicality and efficiency. The flexibility to adjust tower capacity seasonally is one reason these systems are growing in popularity.
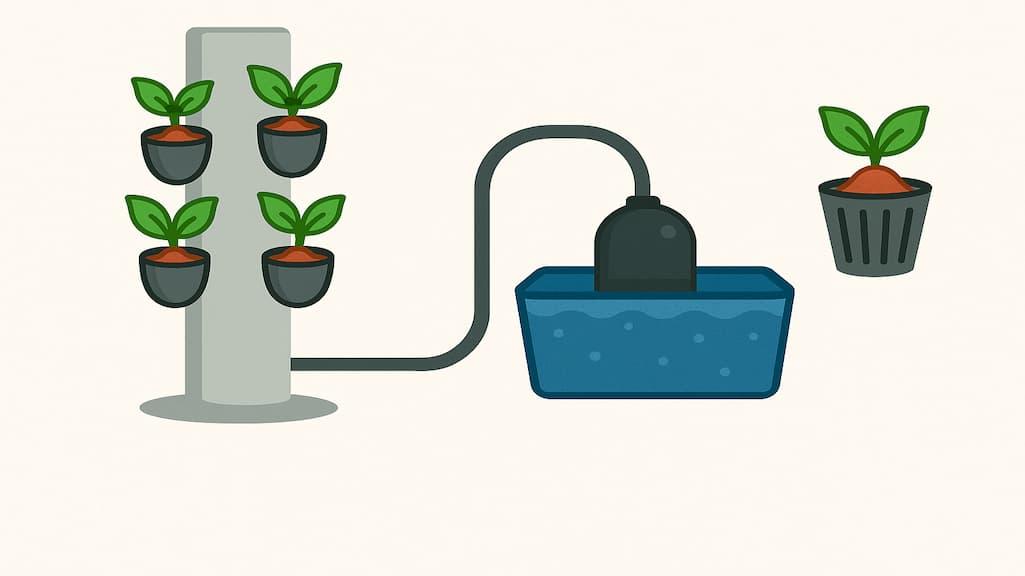
Most DIY towers are built from PVC or food-grade pipes. These materials are durable, lightweight, and easy to modify for plant sites.
A submersible pump circulates nutrient-rich water from a reservoir at the base to the top of the tower, letting gravity distribute the water to each plant.
Net pots are filled with clay pebbles or rockwool cubes, supporting plants while allowing air and water to move through the root zone.
Community gardens often build towers from these materials because they are inexpensive and widely available, making them accessible for large-scale shared projects.
Cut the PVC pipe to your desired height. Drill evenly spaced holes for net pots and smooth any rough edges to avoid damaging plant roots.
Place the pump in the reservoir, attach tubing to deliver water to the top, and check for tight seals to prevent leaks.
Insert net pots into the holes and place seedlings into the growing medium. Ensure that roots have proper contact with the nutrient flow.
Run the system to confirm water circulation. Adjust pump timing and nutrient levels as plants develop.
A gardener in Texas followed these steps to create a backyard tower, producing enough lettuce for weekly family meals without the need for soil beds.
Refresh the nutrient solution regularly to prevent buildup and maintain balanced pH and electrical conductivity (EC) for optimal growth.
Indoor towers require LED grow lights to provide even coverage on all sides. Adequate airflow helps prevent mold and supports healthy development.
If plants at lower levels grow slower, check pump performance and clean tubing to improve water flow. Regular maintenance prevents most common problems.
At a school greenhouse in California, adjusting lighting and checking nutrient balance weekly resulted in improved crop quality and faster harvest cycles.
Leafy greens, herbs, and strawberries are the most suitable choices due to their small root systems and fast growth cycles.
Most home towers are 4–6 feet tall, balancing capacity with easy maintenance.
Hydroponic nutrient solutions designed for water-based growing provide the best results.
Yes, but it should be protected from harsh weather. Outdoor towers benefit from sunlight but need shielding from heavy rain or strong winds.
A basic system usually costs between $50 and $150, depending on size and pump quality.
Weekly inspections of nutrient levels, water circulation, and pump function help maintain steady plant growth.